VGOS - VLBI GLOBAL OBSERVING SYSTEM
The VLBI Global Observing System – VGOS is part of the Global Geodetic Observing System (GGOS) of the International Association of Geodesy (IAG), which integrates different geodetic techniques to provide the geodetic infrastructure necessary for monitoring the Earth system and for Global Change research. It provides observations of the three fundamental geodetic observables and their variations:
- Earth’s shape;
- Earth’s gravity field;
- Earth’s rotational motion.
[Ref.] Image by ggos.org
[Ref.] Image by ggos.org

[Ref.] Image by ggos.org
GGOS (and within it, VGOS) provides the observational basis to maintain a stable, accurate and global reference frame and in this function is crucial for all Earth observation and many practical applications.
In order to improve the VLBI data, it’s necessary to constantly update the equipment to meet the increasingly demanding requirements. In order to always obtain better data quality, the VLBI Global Observing System (VGOS) was created. This system foresees the acquisition of broadband signals, between the frequencies of 2-14 GHz, using electronic equipment and small antennas with a fast-moving capability. To achieve observation accuracy required and improvements in Radio Frequency Interference (RFI), up to four radio frequency bands are placed in the aforementioned range. The more antennas making observations, the higher the spatial and temporal resolution to understand the effect of the troposphere in each station, which, according to simulations, is considered to be the largest source of noise, which is why high bandwidths are required to achieve the necessary precision.
VGOS is being developed to be minimally staffed, remotely controllable, broadband, RFI avoiding, fully digital, fast slewing, and capable of producing VLBI delays with precision of 4 picoseconds (in 4 picoseconds light travels 1 millimeter.) The system is designed to observe continuously.
Since 2005, the International VLBI Service for Geodesy and Astrometry (IVS) has been working on a next generation VLBI system, known as VLBI Global Observing System (VGOS) to achieve accuracies of 1 mm in position and 0.1 mm/year in velocity on global scales, using continuous measurements to obtain uninterrupted time series of station positions and Earth orientation parameters, and a turnaround time from the observations to initial geodetic results of less than 24 h. In the near future, the IVS will change its EOP monitoring to VGOS with a considerable number of dedicated telescopes.
The IVS has been gradually introducing the VGOS systems into the new broadband network as they become available. The initial provisional roll-out plan included broadband test observations in 2015, mainly on the GGAO-Westford baseline. The goal for 2016 was to have one 24-hr VGOS session every week and in 2017 to have several 1-hr sessions for Earth Orientation Parameters (EOP) each day. The pilot project for 2018 was the combination of the 2016 and 2017 observing scenarios using more than ten VGOS stations. In Fig.4, the current VGOS network can be observed.
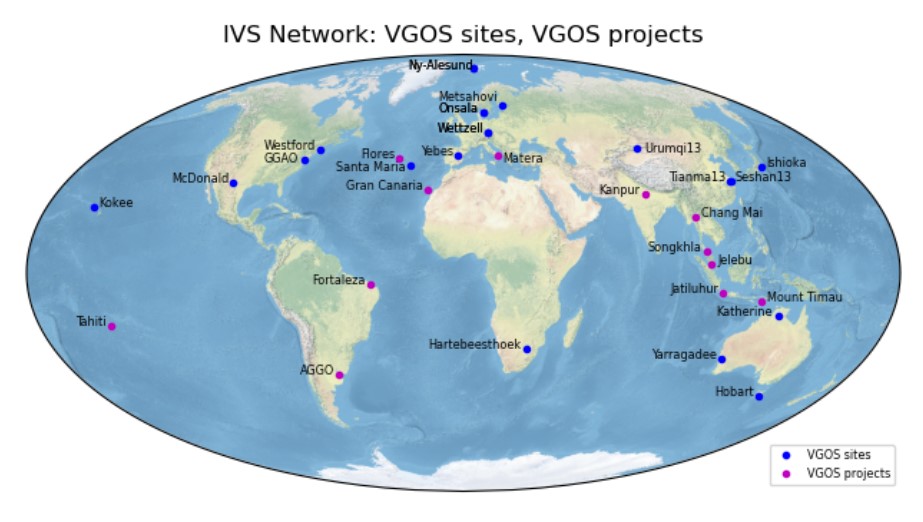
[Ref.] Image by M. Bautista et al.
